 +86 178 5514 5298
+86 178 5514 5298
Leave Your Message
-
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER -
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER -
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER



The concept of an Absorbent Pocket is fascinating yet often overlooked. This innovative design finds its place in various applications, ranging from clothing to healthcare products. An Absorbent Pocket is created using specially engineered materials that can absorb liquids efficiently.
Imagine a comfortable shirt that also keeps you dry. The fabric uses absorbent technology that ensures moisture does not seep through. This is particularly useful in activewear and undergarments. However, the effectiveness of an Absorbent Pocket can vary depending on the material and its intended use.
While this technology is beneficial, it may not always perform as expected. Users sometimes report that the pockets do not hold as much as they hoped. Additionally, some might question their durability after repeated washes. Exploring these aspects reveals both the promise and limitations of the Absorbent Pocket.
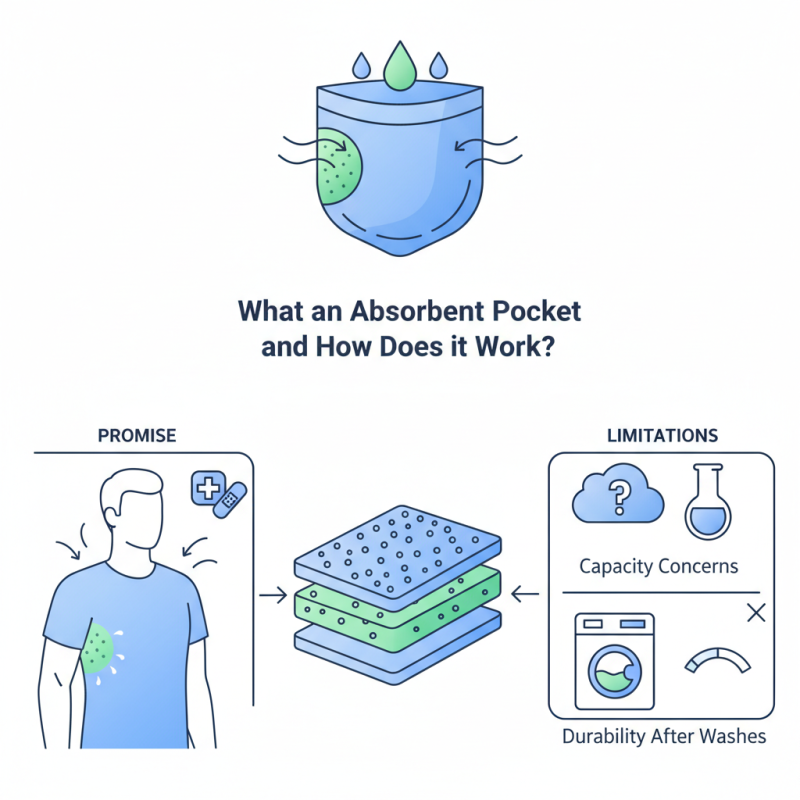
An absorbent pocket is a specially designed insert that captures moisture and keeps surfaces dry. These pockets are commonly found in clothing, accessories, and various products. They serve a vital role in absorbing sweat, spills, or other liquids. Understanding how absorbent pockets function can enhance your experience with everyday items.
The core material of an absorbent pocket typically features multilayer fabrics. These layers work together to trap liquids effectively. The top layer lets moisture through but seals it beneath, ensuring it doesn’t leak. This clever design helps keep you comfortable and protects items from damage.
Tip:
When selecting products with absorbent pockets, check the material quality. High-quality elements enhance absorption and durability.
It’s essential to remember that not all absorbent pockets are created equal. Some may not last as long or perform as well under certain conditions. Reflect on your usage and needs when choosing.
Tip:
Always follow care instructions to maintain the effectiveness of absorbent pockets. Regular washing can enhance longevity but follow guidelines to avoid damaging the material.
Absorbent materials play a critical role in various applications, from healthcare to agriculture. These materials can hold significant amounts of liquid relative to their weight, making them invaluable for products like diapers and absorbent pads. The key properties of absorbent materials include their porosity, hydrophilicity, and absorbent capacity. Studies show that super-absorbent polymers can soak up to 300 times their weight in water, highlighting their efficiency.
The mechanisms that govern how these materials work are fascinating. When liquid comes into contact with an absorbent material, the molecules interact, leading to absorption. This process often involves capillary action, where liquid moves through small spaces within the material. According to a report from the Journal of Applied Polymer Science, fine nanostructures enhance absorption rates. However, not all materials perform equally; some may fail under extreme conditions or prolonged use.
Despite the advancements in absorbent technology, challenges remain. Some materials lose their effectiveness when saturated too quickly. Environmental concerns also persist regarding disposal. A growing focus on sustainability is pushing for biodegradable options, but finding the right balance between efficiency and eco-friendliness is an ongoing challenge. Experimentation and innovation will be key to overcoming these hurdles.

Absorbent pockets have a broad range of applications across various industries, showcasing their versatility. In the medical field, they are often used in wound dressings. These pockets can soak up excess fluids, keeping the wound clean and promoting healing. They offer comfort for patients while also preventing infections in critical environments.
In the automotive sector, absorbent pockets play a role in managing spills. When a vehicle experiences a leak, these pockets can absorb fluids quickly. This helps to maintain safety on the road and protects the environment. However, the challenge lies in ensuring these pockets are made from sustainable materials. It's essential to balance effectiveness with eco-friendliness.
The food industry also benefits. Absorbent pockets are utilized in packaging to maintain freshness. They can extend shelf life by controlling moisture, but sometimes they are not as effective as intended. People might find that some products still spoil quickly. This raises questions about how consistently absorbent pockets perform in real-life scenarios.
Absorbent pockets are innovative structures designed to capture and retain fluids. They work by using materials that can hold moisture effectively. This makes them useful in various applications, from medical devices to clothing. Evaluating their efficiency is crucial to ensure they meet specific needs.
Performance metrics often focus on absorption capacity. This refers to how much liquid an absorbent pocket can hold relative to its size. Testing methods vary. Some use direct measurement, while others assess real-world performance. Understanding these metrics helps users select the right absorbent pocket for their requirements.
Another important aspect is release time. How quickly does the pocket dry out? Effectiveness can diminish if it takes too long to release moisture. An absorbent pocket may seem high-performing but can fall short in practice. This raises questions about design and material choices. Continuous improvement in these areas is essential for better results.
| Absorbent Pocket Type | Absorption Capacity (mL) | Material Composition | Drying Time (hrs) | Cost per Unit ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type A | 150 | Polyester, Cellulose | 2 | 0.50 |
| Type B | 200 | Cotton, Nylon | 1.5 | 0.65 |
| Type C | 180 | Viscose, Polyester | 2.5 | 0.75 |
| Type D | 220 | Polypropylene, Cotton | 1 | 0.80 |

Absorbent pocket technology is evolving. Manufacturers are exploring sustainable materials. These innovations promise to reduce waste and enhance functionality. Natural fibers are being tested. They can perform well while being eco-friendly. This shift is crucial as consumer awareness of environmental issues grows.
There are challenges to consider. Not all sustainable materials perform equally. Some may lack durability or absorbency. The quest for balance between sustainability and effectiveness continues. Researchers are looking for solutions. Innovations in fabric treatments or blends might help.
Future trends will likely focus on biodegradability. Materials that break down without harming the environment are key. Additionally, there may be a shift towards closed-loop systems. Recycling absorbent pockets could become more common. As technology advances, expectations will rise. Consumers will seek products that align with their eco-friendly values. The industry must adapt to these changes.






