 +86 178 5514 5298
+86 178 5514 5298
Leave Your Message
-
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER -
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER -
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER



Choosing the right specimen tube is a critical decision in laboratory settings, significantly impacting the accuracy and reliability of test results. According to a recent report by the International Journal of Laboratory Science, improper specimen tube selection can lead to a 20% margin of error in diagnostic testing, which can severely affect patient outcomes. Various types of specimen tubes are designed to accommodate different sample types and analytical requirements, and their material, additives, and design can influence the stability and integrity of collected specimens. For example, EDTA tubes are essential for hematological analyses, while gel separator tubes are optimal for serum tests. With advancements in laboratory technologies and an increasing demand for precise diagnostics, understanding the nuances of specimen tube selection is more crucial than ever. As such, this guide aims to equip laboratory professionals with the necessary knowledge to make informed decisions, ensuring the highest standards of testing and patient care.
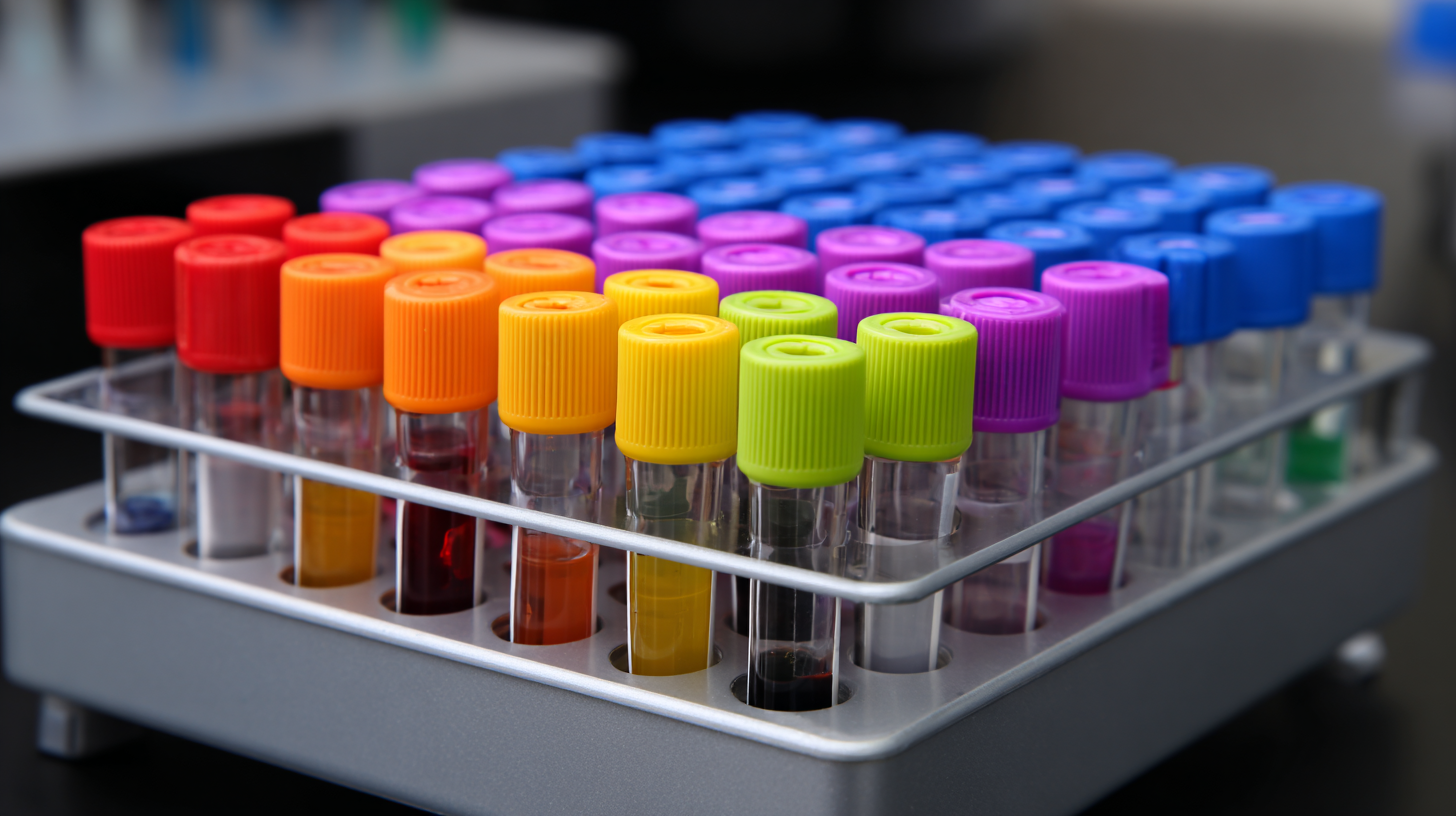
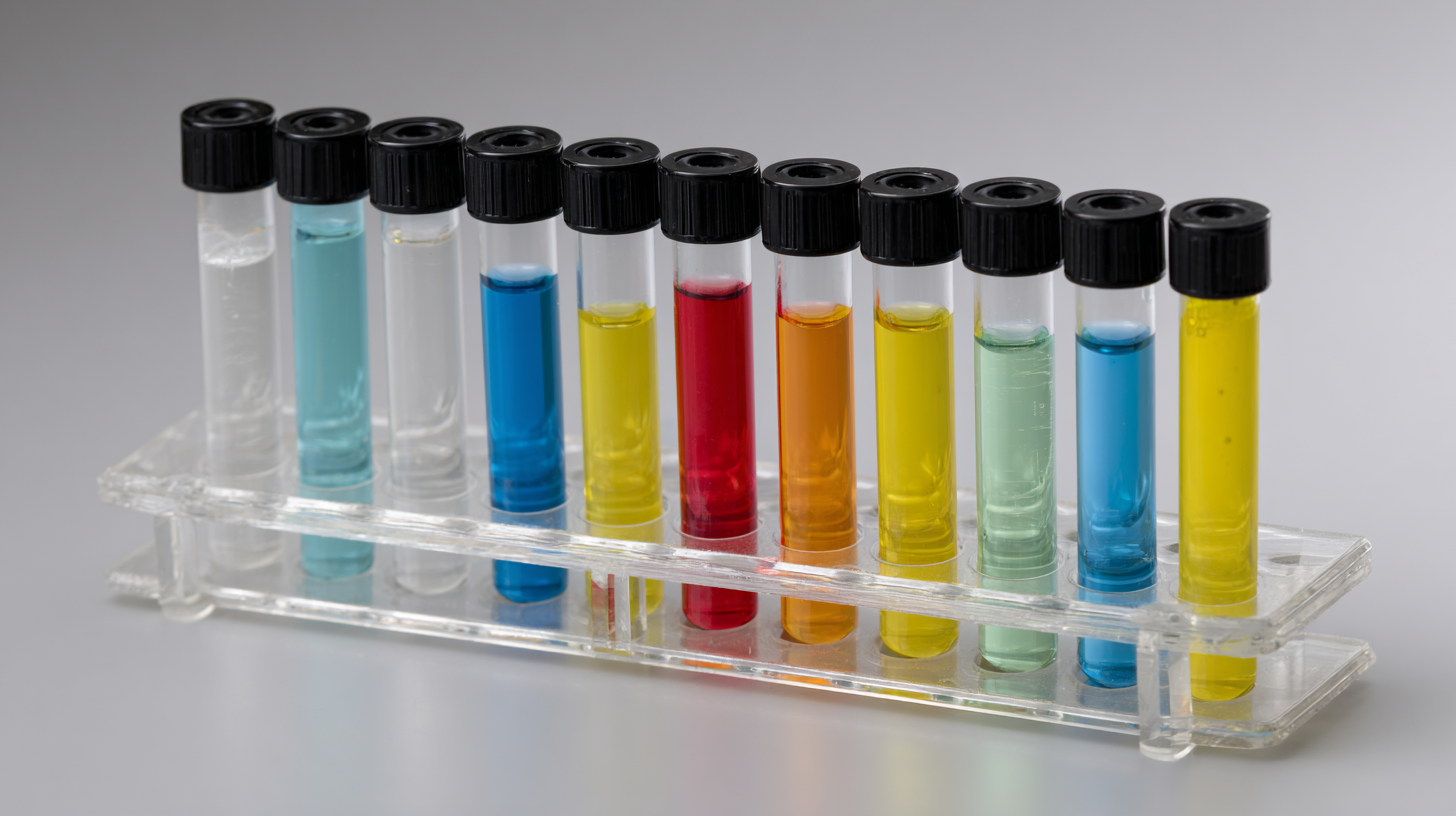
When selecting the appropriate specimen tube for laboratory use, it’s crucial to understand the various types available and their specific applications. Specimen tubes come in various colors, each indicating the type of additive used. For instance, lavender-top tubes contain EDTA, ideal for hematology tests, while green-top tubes, which contain heparin, are preferred for plasma chemistry assays. According to a report by the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), the choice of specimen tube can significantly influence the results of certain tests, making it essential for labs to employ the correct tube type to minimize variability.
Furthermore, factors such as the tube volume and material also play a significant role in test accuracy. Glass tubes, for example, can be advantageous for minimizing the risk of contamination, particularly in sensitive assays. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis highlights that utilizing the appropriate specimen containers reduces the incidence of errors in laboratory results by approximately 20%. Hence, understanding the specifications and applications of different specimen tubes is fundamental for laboratories aiming to achieve high-quality, reliable results in their diagnostic processes.
| Tube Type | Purpose | Additives | Volume (ml) | Color Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDTA Tube | Hemoglobin & Blood Smears | EDTA | 4.5 | Lavender |
| Serum Separator Tube | Serum Chemistry Tests | Gel & Clot Activator | 6 | Gold |
| Citrate Tube | Coagulation Studies | Sodium Citrate | 2.7 | Light Blue |
| Heparin Tube | Plasma Chemistry | Heparin | 4 | Green |
| No Additive Tube | Serology Tests | None | 5 | Red |
When selecting the right specimen tube for laboratory needs, several key factors come into play. One of the most crucial considerations is the type of specimen being collected. Different specimens, such as blood, urine, or tissue, require specific tube materials and additives to ensure proper preservation. For instance, blood samples may need tubes with anticoagulants or gel separators, while urine samples typically require sterile containers. Understanding the requirements for each type of specimen will guide you in making an informed choice.
Tips: Always check manufacturer guidelines for the recommended specimen collection methods. This can help avoid sample contamination and ensure accurate test results. Additionally, consider the volume of the specimen required for testing. It’s vital to select tubes that can accommodate the necessary volume without compromising the integrity of the specimen.
Another factor to consider is the compatibility of the specimen tubes with the testing equipment. Ensure that the selected tubes fit the lab's automated analyzers, as this can streamline the workflow and reduce the risk of errors. Lastly, think about the storage conditions and shelf life of the tubes, as improper storage can impact the quality of the specimens over time.
When selecting specimen tubes for laboratory use, material compatibility is essential to ensure accurate results and maintain sample integrity. Different materials, such as glass and various plastics, have unique chemical and physical properties that influence their interaction with biological samples. According to a study published in the "Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis," polycarbonate and polypropylene tubes demonstrated minimal leaching when storing chemical solutions, making them preferable for aqueous samples. On the other hand, glass tubes are often recommended for volatile compounds due to their inert nature.
**Tips:** Always check the manufacturer's specifications for the tube materials to confirm their compatibility with your specific samples. Furthermore, ensure that the chosen tube meets regulatory standards, as certain materials may interact adversely with specific chemicals, leading to unreliable test results.
In addition, consider the temperature stability of the materials used in your specimen tubes. A report from the "Clinical Chemistry" journal indicates that polypropylene tubes retain their shape and structure better under freezing conditions compared to polystyrene tubes, which can become brittle. This choice is particularly crucial when dealing with samples that require long-term storage at low temperatures.
**Tips:** If uncertain about the suitable tube for your sample, conducting a compatibility test or consulting with material safety datasheets can provide further insight and guidance.
Choosing the right specimen tube for laboratory use is pivotal for ensuring accurate and reliable results in diagnostics and research. One critical aspect to consider is the selection of appropriate additives for specimen preservation. Additives play a significant role in maintaining the integrity of the sample, preventing degradation, and ensuring that analytic results are trustworthy. For instance, according to a report published by the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), the correct use of additives can enhance recovery of analytes by up to 30%, depending on the type of specimen being analyzed.
When selecting additives, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements for the tests being performed. For example, anticoagulants like EDTA are commonly used in hematology to prevent blood clotting, while sodium citrate is preferred for coagulation tests. A study by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) highlighted that the wrong choice of anticoagulants could lead to falsely elevated results in coagulation profiles, emphasizing the need for meticulous selection based on the intended analysis. Understanding these nuances can significantly impact the laboratory's performance and the quality of patient care.

Proper handling and storage of specimen tubes are crucial for maintaining the integrity of biological samples and ensuring accurate test results. According to a report by the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), improper storage conditions can lead to degradation of samples, resulting in up to 30% of laboratory test failures. Specimen tubes must be stored in an environment with controlled temperature and humidity to prevent contamination and ensure the stability of the samples.
Tips for Storage: Always label specimen tubes clearly, including the date, time of collection, and the type of specimen. This practice not only helps in tracking the samples but also minimizes the risk of mix-ups during testing.
When it comes to handling, it is essential to avoid direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. The American Association for Clinical Chemistry (AACC) suggests that most specimen tubes should be stored at temperatures between 2°C to 8°C, especially for sensitive analyses like tests for hormones or infectious diseases.
Tips for Handling: Use gloves when handling specimens to prevent contamination, and ensure that the caps on the tubes are tightly secured after collection. This will help in reducing the risk of leakage and contamination during transport to the lab.







