+86 178 5514 5298
+86 178 5514 5298
Leave Your Message
-
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER -
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER -
 CONTACT NUMBER
CONTACT NUMBER


 The transportation and handling of infectious substances require stringent safety measures to protect both personnel and the environment. Among the key components in this safety framework are UN 2814 bags, specifically designed for the containment of dangerous biological materials. According to a report by the World Health Organization, improper handling of infectious substances can lead to significant health risks and environmental contaminations, with outbreaks linked to transport failures highlighting the urgency for regulated practices. The UN 2814 bag not only meets international packaging standards but also ensures that hazardous biological specimens, such as those containing pathogens affecting humans, are safely sealed during transit. With the increasing focus on biosecurity and the rise in global trade of biological materials, understanding the essential safety protocols related to UN 2814 bags becomes critical. Enhanced awareness and adherence to these guidelines are vital in mitigating risks associated with the shipping and handling of infectious agents.
The transportation and handling of infectious substances require stringent safety measures to protect both personnel and the environment. Among the key components in this safety framework are UN 2814 bags, specifically designed for the containment of dangerous biological materials. According to a report by the World Health Organization, improper handling of infectious substances can lead to significant health risks and environmental contaminations, with outbreaks linked to transport failures highlighting the urgency for regulated practices. The UN 2814 bag not only meets international packaging standards but also ensures that hazardous biological specimens, such as those containing pathogens affecting humans, are safely sealed during transit. With the increasing focus on biosecurity and the rise in global trade of biological materials, understanding the essential safety protocols related to UN 2814 bags becomes critical. Enhanced awareness and adherence to these guidelines are vital in mitigating risks associated with the shipping and handling of infectious agents.
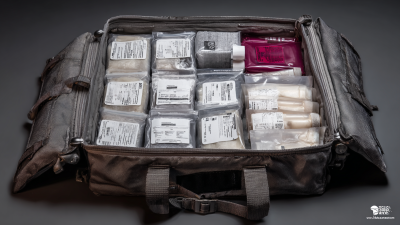
UN 2814 bags are essential for the safe transportation of infectious substances. These bags are specifically designed to contain and isolate materials that may pose a risk to public health, ensuring that potential pathogens are securely enclosed. One of the key features of UN 2814 bags is their robust construction, which typically includes multiple layers of leak-proof materials. This design prevents the accidental release of hazardous contents during handling or transit. Additionally, these bags often come with clear labeling that complies with international regulations, indicating their contents and associated risks, which is crucial for safety during emergency response.
Another important characteristic of UN 2814 bags is their compatibility with various containment systems. Many bags are designed to fit into secondary containment devices, such as rigid outer containers or coolers, which provide added protection against leaks and spills. The bags may also feature color-coded designs to facilitate quick identification in laboratories and transport facilities. These visual cues help workers recognize hazards immediately, enabling them to take swift action when necessary. Overall, the identification features and construction quality of UN 2814 bags play a pivotal role in maintaining safety standards for the handling and transport of infectious materials.
 When handling UN 2814 bags, which are designated for substances posing a high risk of infection, the importance of essential Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) cannot be overstated. According to recent guidelines, PPE should include gloves, protective gowns, face shields, and respiratory protection, particularly in containment level 3 laboratory settings. The European Directive 2000/54/EC emphasizes the need for comprehensive worker protection against biological agents, reinforcing the critical role that proper PPE plays in minimizing exposure risks.
When handling UN 2814 bags, which are designated for substances posing a high risk of infection, the importance of essential Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) cannot be overstated. According to recent guidelines, PPE should include gloves, protective gowns, face shields, and respiratory protection, particularly in containment level 3 laboratory settings. The European Directive 2000/54/EC emphasizes the need for comprehensive worker protection against biological agents, reinforcing the critical role that proper PPE plays in minimizing exposure risks.
In addition to PPE, effective training and compliance with safety protocols are vital when dealing with biohazardous materials. For instance, industry reports suggest that improper handling and transportation contribute significantly to contamination incidents. Adhering to the top safety tips for transporting biohazardous materials—correct classification, secure packaging, and established emergency procedures—ensures that potential hazards are managed effectively. Recent progress in laboratory biosafety underscores the necessity of continuous training and adherence to regulatory requirements, which remains pivotal in safeguarding both personnel and the public.
Transporting infectious materials requires strict adherence to safety protocols to minimize risks. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 300 million units of infectious substances are handled annually, underlining the need for proper procedures. Using UN 2814 bags is crucial, as these specially designed containers provide essential protection during transport. To safely handle and transport these materials, it is vital to follow a step-by-step procedure.
First, ensure that the infectious material is securely packaged within a UN 2814 compliant outer marking. Following this, conduct a thorough inspection to check for any leaks or damages. Proper labeling is imperative, as it alerts handlers about the potential risks associated with the contents. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), nearly 30% of accidents in laboratory settings arise from improper labeling or packaging protocols, which highlights the critical nature of these initial steps.
During transport, maintain specific temperature controls as outlined in the International Air Transport Association (IATA) guidelines. This includes transporting materials in a monitored environment or utilizing refrigerated transport if necessary. Additionally, ensure all staff handling these materials have undergone comprehensive training, with the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) recommending annual refresher courses to maintain high safety standards. By adhering to these procedures, facilities can significantly mitigate the risks associated with transporting infectious materials.
| Procedure Step | Description | Safety Measure | Compliance Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Gather necessary materials, including UN 2814 bags, gloves, and labeling materials. | Ensure gloves are fitted and free of tears. | Follow manufacturer guidelines. |
| 2. Packaging | Place infectious materials inside UN 2814 bags securely. | Check for any leaks or damages to the bags. | Adhere to regulatory standards for packaging. |
| 3. Labeling | Label the bag with appropriate hazard symbols and handling instructions. | Use waterproof labels to avoid smudging. | Ensure labels meet OSHA and DOT requirements. |
| 4. Transport | Transport bags in a secure manner to prevent spillage. | Keep bags upright and avoid stacking. | Follow the predetermined transport routes. |
| 5. Disposal | Dispose of bags according to local regulations for infectious waste. | Use designated waste containers only. | Comply with hazardous waste disposal laws. |
When dealing with UN 2814 bags, which are specifically designed for the transport of infectious substances, it is critical to have a robust emergency response plan in place. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), improper handling of hazardous materials can lead to significant health risks not only for the first responders but also for the public. In the event of spills or accidents, immediate action is essential. The National Institute of Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) recommends that organizations develop a step-by-step protocol that includes evacuation procedures, decontamination measures, and communication strategies to alert necessary agencies.
For effective spill management, facilities should ensure they are equipped with spill kits containing absorbent materials, neutralizers, and personal protective equipment (PPE). Data from the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) highlight that exposure to infectious agents can pose severe health threats, including the risk of zoonotic diseases. Implementing regular training and simulations for staff not only prepares them for real-life scenarios but also ensures compliance with regulatory standards. Engaging in routine inspections and audits of containment measures will further reinforce the safety protocols associated with handling UN 2814 bags in emergency situations.

The handling of UN 2814 bags, which are used for transporting infectious substances, requires adherence to stringent disposal and decontamination protocols to ensure safety. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), improper disposal of these bags can lead to significant public health risks, including the spread of infections. Therefore, it is crucial to follow best practices when managing these materials.
For effective disposal, it is essential to utilize designated biohazard containers that comply with local regulations. Studies show that sterilization methods, such as autoclaving, can effectively eliminate pathogens found in infectious waste. It’s recommended that facilities conduct regular audits of their waste management processes to identify areas for improvement, as outlined by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
**Tips:**
1. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) when handling UN 2814 bags to minimize risk of exposure.
2. Train staff regularly on the protocols for decontamination to ensure compliance with safety standards.
3. Keep a log of all waste disposal activities to monitor practices and maintain accountability.